Success in the Art of Pavement Construction, Steve Burton and Phil Critchton from Steintec
Planting and hardscape work close together and often lead to very technical planning processes.
The arch shaped pattern of pavement have a structural function. If the path has a slope, the arches are created in the opposite way (up the hill) to take on the loads of vehicles that use the road.
Unlike in Switzerland and other parts of Europe, not many of the arch shaped patterns exist in the UK anymore. Mainly because the industrial. revolution and development of “better” and more “fashionable” solutions.
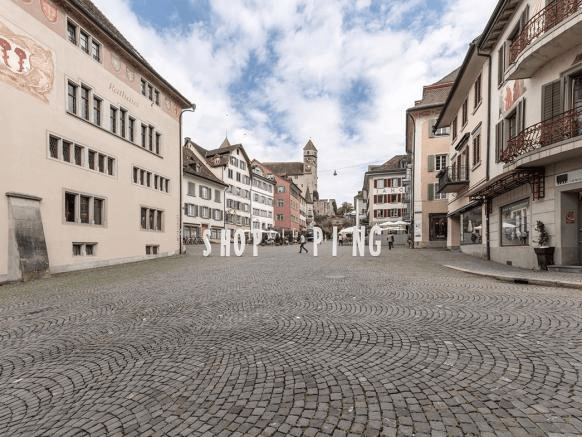

Arch-shaped paving in my hometown
Paving starts suffering from different issues/impacts over time.
Cuases of failure can be:
- Bad design
- Wrong methods -> workmanship issues
To prevent workmanship issues we have know that we need to make sure that appropriate methods are used on site!
Landscape Architects usually can refer to guidance of manufacturers on. how to use materials correctly on site.
Extract of a Construction Plan with specific directions for the contractor
Pavement Design
We have to make sure that the pavement build ups and materials are defined, correct and implementable on site.
Sustainability
- longevity
- need of maintenance
- reusability
Bound vs. unbound construction
Bound construction only fails once. So it should always be planned to be able to take slightly more than the max. required loads.
Unbound construction gets worn down when heavily used but it dies’t fail right away
Unbound materials in Switzerland: would be good to start researching or contacting companies that I’m familiar with back in Switzerland to include some of their approaches in my design/planning processes in the UK.
3 types of paving element
- Full depth sets -> moving vehicles put force in the moving direction and downwards, which creates a rotational effect.
- Slabs -> Force downwards on one side and “counteraction” on the other side
- Shallow sets -> both of the above combined
Movement joints are always important to absorb material expansions/compressions
Moisture
Moisture can bring range of problems and damages to pavings: Frost damage/damage through temperature changes, permanent water marks

Permeable material underneath the paving is essential to prevent damages caused by moisture. Using bigger grained mortar instead of sand/cement mortar can increase permeability
Importance of standing by your specification
Value engineering -> You choose the right product to meet the requirenments based on performance
The contractor chooses the material based on costs/profit.
Leave a comment